The integration of artificial intelligence in human resource management (HRM) is transforming traditional recruitment and workforce strategies. From AI-driven hiring processes to bias detection in recruitment, organizations are leveraging advanced technologies to enhance efficiency and decision-making. This report explores the role of AI in HR recruitment, ethics, and future trends, highlighting its impact on employee engagement, automation, and workforce management.
The Role of AI in Human Resource Management: Recruitment, Ethics, and Future Trends in HRM
Table of Contents
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence has evolved over time and has taken a major role in altering the business environment by inducing faster adoption of AI driven technologies which can be operated at scale without compromising on the outcome, at the same time with wider adoption the costs for such solutions have considerably decreased, post covid boom in business have also played a pivotal role for such a trend. Every aspect of business, covering all business functions, is now capable of being powered by AI in some form or other. Human Resources divisions are no stranger to the same, with increasing workforce and diversity and job requirements, the HR division of companies has started to rely on AI in their operations, with sufficient data and computational capacity, AI can power the HR function to play an extensive role in shaping the organization. Personalization is the key driver for AI adoption in this domain because humans are different and so are their expectations. The entire concept of AI is not based on a single theoretical framework but built over several algorithms, Machine Learning is the key backbone, which has led to the creation of predictive algorithms that learn from the data that we feed into them. Current AI solution is formed based on a neural network which mimics the way human mind operates, one of the significant drawbacks initially was the programming languages in machine language. But with natural language processing, normal words are easily converted into binary numbers in real time. For HR, AI solution providers utilize Decision Theory to optimize hiring decisions by taking into account multiple factors. Cognitive Computing is another area where simulation of human reasoning is done to make personalized feedback to employees. We conducted a primary research asking people who have already been employed their take on AI. We also interviewed three professionals, Ms. Shruti Waghmare, Lead HR at Fresh Gravity, Ms. Nang Chasanya Thamoung, and Srujana Reddy, a former HR professional.
NOTE: Looking for the Best Assignment Help Online? Contact us today!
Check all the subjects we help with ->
IMPORTANT TIMELINES FOR AI IN RECRUITING
- Early 2000s: Emergence of Applicant Tracking Systems
- Mid 2010s: AI integration in Resume Parsing and Screening
- Late 2010s: Chatbots and Conversational AI
- 2020s: Advanced AI tools for Bias Detection and DEI Optimization.
End-to-end solutions are under development, which requires minimal human intervention and resources, which can be expected to be commercialized in the later part of this decade.
KEY DRIVERS OF AI IN RECRUITMENT:
1. Improvement in the Algorithms of Machine Learning The sophisticated deployment of supervised and unsupervised learning models can be used for precise candidate-job matching based on historical and behavioral data.
2. Advances in Natural Language Processing (NLP) These new models, like BERT and GPT, facilitate unstructured data processing for such cases as resumes and job descriptions. These models thus allow for semantic analysis, thus ensuring that for every job opportunity, the candidate is contextually accurate in matching to the job requirements, rather than being dependent solely on a keyword-based search.
3. Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics in Recruitment, Predictive analytics-tells how much of a winning candidate the candidate remains and is determined by past hiring trends and performance metrics. Prescriptive analytics is helpful as it prescribes the actions to be taken to refine shortlisting and hiring, thus having better outcomes.
4. Bias Detection and Fairness Algorithms Integration of fairness-aware learning techniques with algorithmic auditing tools into AI systems has enabled identification and control of unconscious bias in recruitment processes. This is meant to keep up with equity hiring practices in DEI efforts.
5. Cognitive Computing and Decision Theory Cognitive computing solutions mimic human reasoning in solving tough recruitment challenges, including assessing culture-fit or weighing conflicting candidate attributes against each other; multi-objective decision-making frameworks are engaged for balancing the different multiple requirements such as qualification, experience, and dynamics of team in the recruitment scenario.
LITERATURE REVIEW:
Artificial intelligence is transforming the recruitment process. The process of recruitment is changing with artificial intelligence, and it is changing all processes of recruitment, making it efficient, free from human biases, and solving the problem of talent acquisition. It includes applicant tracking systems, natural language processing, and talent analytics that make the work of resume screening, matching candidates, and scheduling, among others, which were earlier time-consuming (Lundvall, 2022). These innovations allow organizations to concentrate on strategic hiring decisions and reduce time-to-hire while improving the candidate experience overall. AI also helps in scalability so that firms can manage big applicant pools with greater accuracy and fairness (Upadhyay & Khandelwal, 2018). Yet, AI recruitment is surrounded by major issues. Lack of trust in AI is an issue among many human resources professionals. They often consider AI technology to be a threat to their positions. Furthermore, many human resources professionals have no technical skills that are usually required for proper implementation of AI (Lundvall, 2022)
Ethical considerations, from algorithmic biases to issues of data privacy and even the opacity of decision processes, complicate AI integration. For example, biased training data ensures that some discrimination is extended, whereas the purpose behind AI implementation is to include and not exclude (Hurlburt, 2017; Eubanks, 2018). Research suggests that AI is best suited for repetitive tasks, but human judgment is still indispensable.
Insights from the Interviews and Primary Research
1. HR software for HR Software for employment purposes is a necessity.
As mentioned by Nang Chasanya Thamoung, a HR services provider, AI-based HR software has an important role in automating routine HR tasks. Such tools improve operations, from resume screening to workforce planning and resolving employees’ questions. According to Nang, it is important for the HR team to enlist tools like Workday to streamline its recruitment process, improving accuracy and freeing them from manual work. AI chatbots help improve labor relations and HR processes by providing immediate support to employees. There are reports that predictive analytics within HR systems can help an organization identify attrition risks, develop customized training programs and focus on the achievement of strategic goals while enhancing employee satisfaction. These innovations make HR departments strategic partners in the growth of organizations.
2. AI in recruitment: AI in recruiting.
“The hiring process will be completely changed by AI,” Srujana Reddy, a former HR professional, said. AI tools have become indispensable for an effective and efficient recruitment process, reducing biases and improving results exponentially. Srujana pointed out how tools like HireVue assess candidate skill fit through AI-based analytics and enable recruiters to make faster and more informed decisions. Predictive analytics has become an integral part of recruitment, enhancing efficiency and accuracy while also ensuring fairness. A number of studies indicate how AI reduces time-to-hire by automating screening of candidates, scheduling interviews, and communication. This does not only enhance the candidate experience but also offers actionable insights for HR teams in attracting the best.
3. Employee Self-Service Portals, the employer has to establish to monitor and control a self-service portal for the user’s self-service portal.
HR Lead Shruti Waghmare explained the role of self-service portals in enabling employees and simplifying HR processes.
According to Shruti, such self-service access portals allowed the employees to update their personal details and view pay slips while being able to apply for leaves, all by themselves. The user experience herein has been enhanced further by effectively resolving employee queries at the instant through the introduction of an AI-based chatbot. This has been further confirmed through secondary research that self-service portals have reduced the administrative workload by leaps and bounds for HR teams. A key benefit of Accessibility and Convenience would be higher employee satisfaction and productivity, and alignment of HR functions with organizational objectives. This report is based on both primary interviews with HR professionals and secondary research from industry studies underscores the pivotal role of technology in HR. From automation and artificial intelligence in business processes to self-service tools, technology enables HR teams to focus on strategic goals, improve efficiency and deliver superior employee experiences. As HR technology evolves, organizations must stay abreast of the latest innovations to maintain a competitive edge in talent management.
How would you rate the Reliability of AI in the recruiting process?
This primary research represents a multi-dimensional view of the recruitment landscape, which is changing and characterized by growing anticipation for AI integration, tempered by pragmatic concerns and strong emphasis on ethical considerations. A striking majority of 79.2% of respondents believe that AI will eventually replace human recruiters, which is a paradigm shift in talent acquisition. However, this displacement is not absolute. Instead, the study unveiled a future where human-AI collaboration works with one’s strengths.
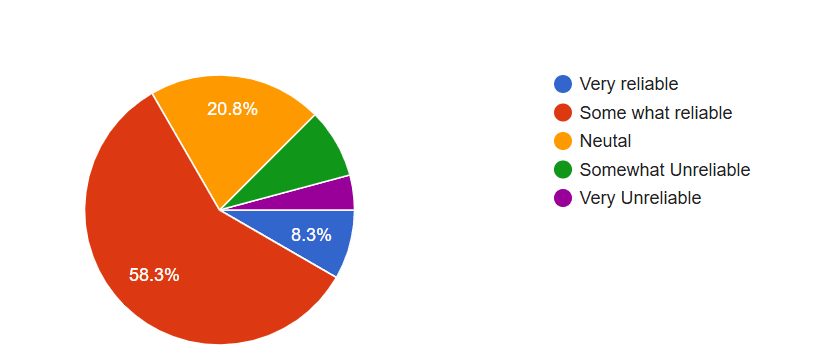
How would you rate the Reliability of AI in recruiting process?
Human responsibility in recruitment will still largely be expected in the judgmental skills and interpersonal competencies areas. It is in such areas that the ethical and legal considerations were seen to be the most crucial responsibility of humans at 54.2%. It simply meant that human oversight will be required to call out fairness, transparency, and accountability by AI-driven recruitment. Furthermore, building relationships with the candidates is 25% which means more emphasis on empathy with candidates, on effective communication, and individual needs that the company wants to bring to their organization. Last but not least, the final decision in the talent acquisition process falls within 8.3% and also depends much on the human factor in order to conclude whether or not a candidate is best suited for the job.
Interestingly, while people may still highly believe in the AI futures’ dominance, a distinct reservation exists on current AI reliability. There’s “only somewhat reliable,” and about 58.3 percent of people attribute it to AI tools with regards to automating task processes or analyzing data; it suggests that most may view with skepticism due to proper considerations on algorithm bias issues standing at 62.5 percent. The heavy dependence on accurate data (75%) also underlines the need for robust data management practices and the potential for skewed outcomes if data is incomplete or biased.
Ethical considerations dominate the findings, and among them, the most relevant one is the candidate’s privacy, at 54.2%. The responsibility of organizations is also here to ensure that AI tools are used in a way respectful of individual rights and not compromising sensitive information. Here lies the implicit call for more transparency in AI algorithm decision-making, for explainable AI, and for mechanisms to explain AI-driven assessments to candidates so they can dispute them, if needed.
Benefits from AI in recruitment are undeniable. Main advantages include faster hiring processes (66.7%), improved candidate screening (54.2%), and increased efficiency, which can lead to more extensive reach. Potential for human bias reduction was also noted (33.3%), but it must be understood that AI, by itself, is not objective and inherits the bias of the data it has been trained on. Potential benefits: both cost efficiency 50% and better candidate engagement 16.7%; AI would allow a better experience for candidates, and there would be better resource optimization.
However, the road to AI implementation is not an easy one. The greatest challenges in terms of cost of implementation are that 45.8% is a very high cost for any organization. In addition, the need for the entire HR team to undergo comprehensive training is 50%. The ability to customize to unique roles is limited at 29.2%.
Advantages of AI in Recruitment and HRM
There are multiple significant advantages of AI in Recruitment. Some of them are qualitative, while others are quantitative. The use of AI positively affects operational efficiency and reduces churn, which leads to a reduction in cost, saves lots of time, and reduces manual efforts. It also improves the decision making process if the data used to train it is significantly diverse and credible. AI also significantly improves the experience of the candidates.
1. Improvement in Operational Efficiency
From our conversation with the HR of Capgemini, Srujana, we got the following insights on improved operational efficiency post-implementation of AI in recruitment-
- Their time to hire reduced from 30 days to 15 days on average, which is a significant reduction of 50%.
- They were also able to successfully reduce their cost by up to 40% by automating their initial screening process and scheduling process.
- The AI chatbots reduced manual work significantly by handlingthe FAQs part.
2. Improved Decision-Making Process
AI reduces guesswork and improves job fit by predictive analysis. It uses historical data to decide upon the ideal characteristics or mapping. It also reduces biases by making the resume anonymous by removing names, demographic information, etc. A good example of this practice is Unilever’s recruitment process.
3. Improved Candidate Experience
Companies use AI to personalize and improve the candidate’s journey. This also has an impact on churn. It significantly improves the speed of the process and makes it more transparent and unbiased. This ensures that the candidates are not having a black hole experience.
4. Better Scalability
AI has made the hiring process way more scalable, especially the initial resume screening. It is almost impossible and very time-consuming for an HR professional to go through the huge scale of resumes submitted for each role. AI makes this process quick and easy by analyzing the initial gamut of resumes and forwarding only a few relevant ones for the further process.
5. Adherence to Standards and Laws
AI helps the company to adhere to the standards and laws in their recruitment process. AI like Eightfold AI flags issues that are related to non-compliance and makes sure that the process aligns with the global standards.
Challenges of AI in Recruitment and HRM
The impact of AI on recruiting has created a remarkable revolution in speed and accuracy in the process of recruitment. The harmful but unavoidable downside of AI adoption is the dramatic challenge that organizations need to overcome by influencing the ethical, effective, and sustainable use of AI.
1. Algorithmic Bias and Fairness Concerns
One of the significant challenges brought by AI into the recruitment world involves algorithmic bias within the system. Most of the AI systems usually base their judgments on historical data, thereby becoming inadvertently biased due to past prejudices. For instance, Amazon’s AI recruitment system was not neutral as to the gender issue, whereby men were favored for the technical positions while recruiting based on training data that had skewed the results. Such biases would negate diversity and inclusion in arbitrary hiring.
2. Problems Concerning Scalability and Interoperability
The integration of AI tools with existing Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) can be very challenging, especially in older organizations with legacy systems. When AI outputs from traditional HR processes do not match, inefficiencies are created, generating delays at times in the recruitment process.
3. Costs and Barriers to Adoption
Most artificial intelligence solutions are expensive and require entrepreneurship training, which makes adoption even more problematic for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Such costs tend to be a no-man’s land for many organizations to a large extent, for they prove difficult to justify in that retroactivity of investment becomes hazy.
4. Cybersecurity and Privacy Risks
AI systems have to process large amounts of sensitive personal data like resumes, recordings of interviews, and background checks, which raises significant cybersecurity and privacy challenges and also concerns among candidates.
5. Explaining Transparency and Explainability Issues
The “Black-Box” nature of most AI models presents HR practitioners with a problem. Emerging on the scene, such AI does not make things easier, for without understanding how AI reaches a judgment, it is difficult to win stakeholder trust.
The Future of AI in Human Resource Management
The future of Human Resource (HR) department is on the verge of being revolutionized by Artificial Intelligence (AI). It can automate repetitive tasks, improve decision-making processes, and provide valuable insights into employee behavior and organizational trends. With companies across the world investing in AI to streamline operations, the HR department is using this technology to improve recruitment, training, performance management, and employee engagement.
AI in Recruitment: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Modern HR Practices and Talent Acquisition
AI-driven tools are revolutionizing recruitment by automating candidate sourcing, screening, and assessment. For instance, companies like LinkedIn and HireVue use AI to analyze resumes and identify the best candidates based on job requirements. AI-powered chatbots, such as those used by IBM’s Watson Recruitment, engage with candidates, answer their queries, and schedule interviews, saving time and effort for HR professionals.Moreover, AI reduces unconscious bias in hiring by basing assessment solely on objective criteria. For example, Unilever uses AI to test candidates through online games and video interviews. The system analyzes facial expressions, tone, and choice of words to predict whether a candidate would be suitable for a job, thus providing a just and inclusive process of hiring. This has ensured that diversity and efficiency have been realized in Unilever’s hiring process.
Training and Development
AI enhances employee training by offering personalized learning experiences. Platforms like Coursera and Degreed utilize AI to recommend tailored courses based on individual career goals and skill gaps. IBM’s AI tool, Watson, provides real-time feedback and suggests resources to employees during their training sessions, ensuring they gain relevant skills efficiently.
Moreover, AI-based virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) simulations are increasingly being used for experiential learning. For instance, Walmart uses VR scenarios to train employees in customer service and handling difficult situations. This experiential learning approach helps the employees feel confident and perform better.
Ethical, Legal, and Regulatory Framework for AI in Recruitment
Artificial intelligence is transforming recruitment by making it smoother and increasing data-driven decision-making. However, as organizations increase the adoption of AI in hiring, it is imperative to keep in mind the ethical, legal, and regulatory considerations so that the adoption of AI is fair and responsible.
Ethical Considerations
AI in recruitment must focus on being transparent, accountable, and fair. Transparency refers to making the role of AI in decision-making clear to the candidates and ensuring that algorithms are understandable. Explainable AI (XAI) frameworks are critical to dealing with the “black-box” problem, whereby decisions seem to be made without an insight into how or why they were reached. Human oversight is necessary in validating AI-driven outcomes, including mitigating risks from possible errors.
Legal Frameworks
Governments globally are formulating laws related to AI in recruitment activities. In Europe, the General Data Protection Regulation mandates data transparency and protects candidate privacy, and the California Consumer Privacy Act in the United States offers similar protections. The Equal Employment Opportunity guidelines are equally important to ensure fair hiring practices. For example, regulations like the EU AI Act focus on categorizing AI systems by their risk levels and hold individuals liable for high-risk applications, such as recruitment. These laws ensure AI adoption aligns with legal standards and fosters trust among stakeholders.
Conclusion
Bias is one of the most critical challenges in AI-driven recruitment. Algorithms trained on biased data may perpetuate discrimination and undermine diversity and inclusion. Companies can counter this by conducting fairness audits, using diverse datasets, and employing adversarial testing to identify and rectify biases. Techniques like Fairness Impact Assessments are becoming standard practices for organizations committed to ethical AI deployment, will enhance the recruitment process without infringing on ethical values or rules, given a commitment toward transparency in the strong framework.
References
Ahmed, H. K., Abdelhay, S., Marie, A., & Abdulrahmin, N. F. (2024). Artificial Intelligence applications in the recruitment process: Opportunities and challenges. European Chemical Bulletin, 12(7), 1008–1019. https://doi.org/10.48047/ecb/2023.12.7.77
Ore, O., & Sposato, M. (2022). Opportunities and risks of artificial intelligence in recruitment and selection. International Journal of Organizational Analysis, 30(6), 1771–1782. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOA-07-2020-2291
Blumen, D., & Cepellos, V. M. (2023). Dimensions of the use of technology and artificial intelligence in recruitment and selection (R&S): Benefits, trends, and resistance. Cadernos EBAPE.BR, 21(2), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1590/1679-395120220080
Al-Alawi, A. I., Al-Hadad, A. A. N., Naureen, M., & AlAlawi, E. I. (2021). The role of artificial intelligence in recruitment process decision-making. In 2021 International Conference on Decision Aid Sciences and Application (DASA) (pp. 197–202). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/DASA53625.2021.9682320
Khan, S., Faisal, S., & Thomas, G. (2024). Exploring the nexus of artificial intelligence in talent acquisition: Unravelling cost-benefit dynamics, seizing opportunities, and mitigating risks. Problems and Perspectives in Management, 22(1), 462–476. https://doi.org/10.21511/ppm.22(1).2024.37
Also Check These Samples:
- Analysis of Work Environment at KPMG
- Impact of Consultancy Skills | Professional Communication and Consultancy Skills Assignment
- HRM Assignment Example – Case Study on La Gusto Coffee

