This is a case study of Toyota’s global strategy and competitive advantage built over the years. We have discussed the history of Toyota, its worldwide presence, and its market positioning, as well as a thorough discussion on internationalization, supply chain management, and marketing strategies adopted by Toyota Motors.
Note: Do you need any Assignment Help at affordable prices? Contact us!
A Case Study on Toyota’s Global Strategy and Competitive Advantage
Table of Contents
Introduction
The automotive industry is characterized by fierce competition with changing consumer preferences and a global footprint that spans continents. Toyota is one of the global giants that consistently comes to the forefront of quality, innovation, and market leadership. This assignment develops fascinating the world with global strategy and adds the ability to maintain a formidable competitive advantage on the global landscape (Kotabe & Murray, 2020).
Toyato’s global strategy holds significant relevance to the context of internationality. Toyota is not just an automaker but a hallmark of the company that strategically positions itself in the highly competitive and dynamic industry. This journey comes from Japan when the company humbly started and became one of the largest and most respected automobile manufacturers and became a testament to the power of astute global strategy. This case study also offers valuable insights for students and their professionals alike (Khan, 2019). Toyota’s success story is deeply rooted in a well-crafted global strategy that spans diverse dimensions and understanding Toyota achieved and maintained the global dominance that is not only intriguing with academic exercise but makes it instructive for business leaders and policymakers. The global automotive industry serves as a microcosm of international business challenges. This will navigate diverse markets and cultural landscapes and manage complex supply chains and technological disruption. Examining Toyota’s global strategy will give me invaluable lessons about adaptability with resilience and leadership in a global context. This assignment also begins by providing a comprehensive background of Toyota including evolution and current market position (Madoh et al. 2019). This background helps to set the stage for understanding with foundations of the global strategy of the company. Introducing theoretical framework with analysis and drawing to relevant topics and theories from the course includes internationalization strategies. These theories serve as a lens through examining Toyota’s strategic choices. These sections will develop into Toyota’s global strategy and explore internationalization strategies, supply chain management, and marketing strategies. Analyzing strategies will help to understand market dynamics and competitive advantage on a global scale using real-world examples and data that will illustrate key points. These assignments will summarise the key findings and offer many recommendations based on the analysis. The insights will serve as valuable sources for anyone interested in understanding and applying effective global business strategies. Embarking on the journey by Toyota’s global strategy and invited to explore the world of the most iconic and globally influential brands in the automotive industry (McMillan, 2019).
You may also like reading Supply Chain Management of Samsung: Case Study on Advanced Inventory Management Techniques
Background and Overview
History
Toyota was established by Kiichiro Toyoda in 1937. The company spreads its roots to the Toyoda Automatic Loom Works that is a textile machinery manufacturer and diversified into the automobile industry. Toyota’s journey began with its production of passenger cars and launched its Model AA in 1936. The outbreak of World War II halted temporarily many automotive operations and shifted its focus to support the Japanese war. Post-war the company again resumed its production of cars and set the stage for global aspirations. In the 1950s Toyota introduced the iconic Land Cruiser and made the first generation to international expansion. Toyota’s foray into the American market with an introduction to the Toyota Crown in 1957 became a milestone and laid the foundation for its global presence (Ondeng, 2020). The 1960s witnessed further expansion as the Toyota Corolla made and became the best-selling car. The company’s commitment and innovation became most evident while launching the Toyota production system in the 1970s. This approach revolutionized manufacturing efficiency and quality. This dedication makes continuous improvement and quality control that helps to become a hallmark in the corporate culture of Toyota. Toyota stands as a global giant in the automotive industry in over 170 countries. The company diversified its operations beyond automobiles including robotics and financial services with mobility solutions. The history of Toyota reflects its remarkable evolution from a domestic automaker to a global powerhouse with its quality, reliability, and sustainability (Ayad et al. 2021).
Global Presence and Market Position
Toyota’s Global presence is a testament to its Internationalisation strategy. The company’s established manufacturing facilities with sales offices across the globe and extensive footprint ensure that Toyota can meet local demands effectively by contributing to the economy of the countries in which it operates. Even the regional focus becomes an element of global strategy. In North America, Toyota has grown to become the largest automaker with a strong presence in the United States (Gupta & Govindarajan, 2019). Even investment in the area of manufacturing facilities and research development centers to its market position. Even in Europe, The company embraced innovative approaches to sustainability. Hybrid technology helps to reach the main point. The introduction of the Toyota Prius in Europe makes a groundbreaking hybrid vehicle that exemplifies the company’s commitment to environmental responsibility and cutting-edge technology. Even Asia remains a significant market for the company and improves the brand’s reputation with quality and reliability. This helps to maintain a strong presence in countries like India, Thailand, and Indonesia. Toyota’s expansion with diverse markets like Africa and Latin America demonstrates its ambition for global growth (Vijaya & Rahayu, 2021).
Overview of Product Range
Compact cars robust SUVs and hybrid vehicles are known for producing a wide variety of models that cater to different customer preferences. Iconic models like the Toyota Camry, Toyota Corolla, and Toyota RAV4 have profound homes in countless driveways around the world. Key divisions including Toyota Division, Lexus, and commercial vehicles make new ranges to diverse needs of consumers. The Lexus exemplifies Toyota’s pursuit of innovation and Luxury that offers a range of high-end vehicles with cutting-edge technology designs. Even the commitment to innovation extends its development of electric vehicles and hybrid technology. The Prius has instrumental shapes for the future of environmentally friendly transportation. The Toyota Mirai also has a hydrogen fuel cell that is dedicated to sustainable mobility. We will develop an analysis of Toyota’s global strategy with competitive advantage. It is vital to comprehend the company’s historical journey to expansive global reach. The breadth of product offerings forms backdrops against access to strategic decisions in the global automotive arena (Alavi et al. 2020).
Theoretical Framework
Analysis of Toyota’s global strategy and competitive advantage will employ a theoretical framework based on key topics such as Internationalisation strategies, Supply chain Management, and Marketing Strategies. These topics help to understand and achieve by maintaining global prominence (Ichijo & Kohlbacher, 2020).
Internationalisation Strategies
This is the core concept of global expansion. The company while entering and making a global presence in international markets has been made methodical and strategies. Toyota implements a diverse range of strategies that help to adapt to diverse markets and navigate complex global dynamics. The best theoretical model is the Uppsala Internationalisation Model. This model suggests how companies can increase international commitment over time and starts with activities and familiar markers must expand to more distant and unfamiliar. Toyota’s journey will align with the model and begin exporting vehicles establish local subsidiaries and production to various regions and reflect a systematic approach to global expansion (Mahdy, 2020).
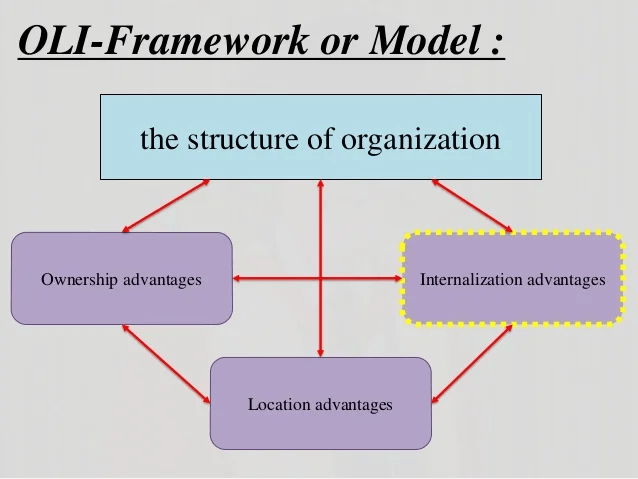
Another theory is the OLI model that was proposed by John Dunning. This model posits internationalization based on advantages and firm on ownership advantages, and location-specific advantages. Toyota’s internationalization strategies will influence ownership of advanced automotive technology and the quest for favorable market conditions with the desire to internalize its operations for greater control (Madhani, 2020).
Supply Chain Management
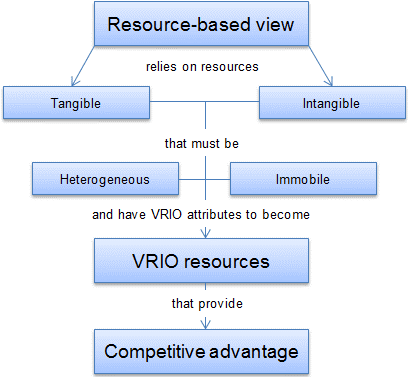
This is renowned for its efficiency and adherence to lean production and principles. Just-in-Time and Kanban systems derived from the Toyota Production System and influenced by reshaping manufacturing practices worldwide. The RBV theory also provides insights into the competitive advantages arising from its unique, valuable, and non-substitutable resources. Toyota’s effective use of lean manufacturing practices will develop and integrate resources within the supply chain operations exemplify its theory and pursuit of waste reduction and continue improvement with involvement and alignment with the RBV framework.
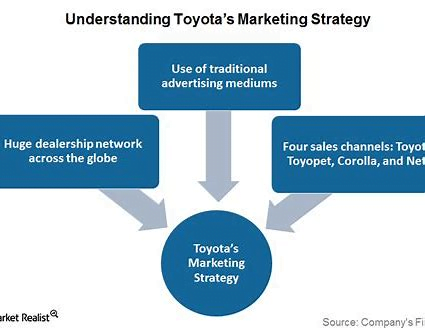
Marketing Strategies
This plays a vital role in the global strategy of the company while it adopts diverse marketing strategies to cater to different consumer segments with preferences and cater to different consumer segments across the globe. Our essential concept is market segmentation. This approach involves a heterogeneous market with more manageable segments based on characteristics. Toyota’s strategy and production of a variety of vehicles can compact on luxury models and align with effective market segmentation that helps to meet diverse consumer needs. Even the BCG matrix helps in marketing and classifies a company’s product portfolio into four diverse categories such as stars, cash cows question marks, and dogs. Stars have with high market share with high growth (Helmold & Terry, 2021). Cash cows with high market share with low growth, Question marks with low market share and high growth. Dogs with low market share and low growth. The company’s diverse product range positions across these categories allowed it to balance its portfolio and manage its resources strategically. We will use insights associated with internationalization strategies. Supply chain management and marketing strategies assess global strategy and competitive advantage. This approach will enable me to gain a deep understanding of what excelled in the highly competitive global automotive industry.
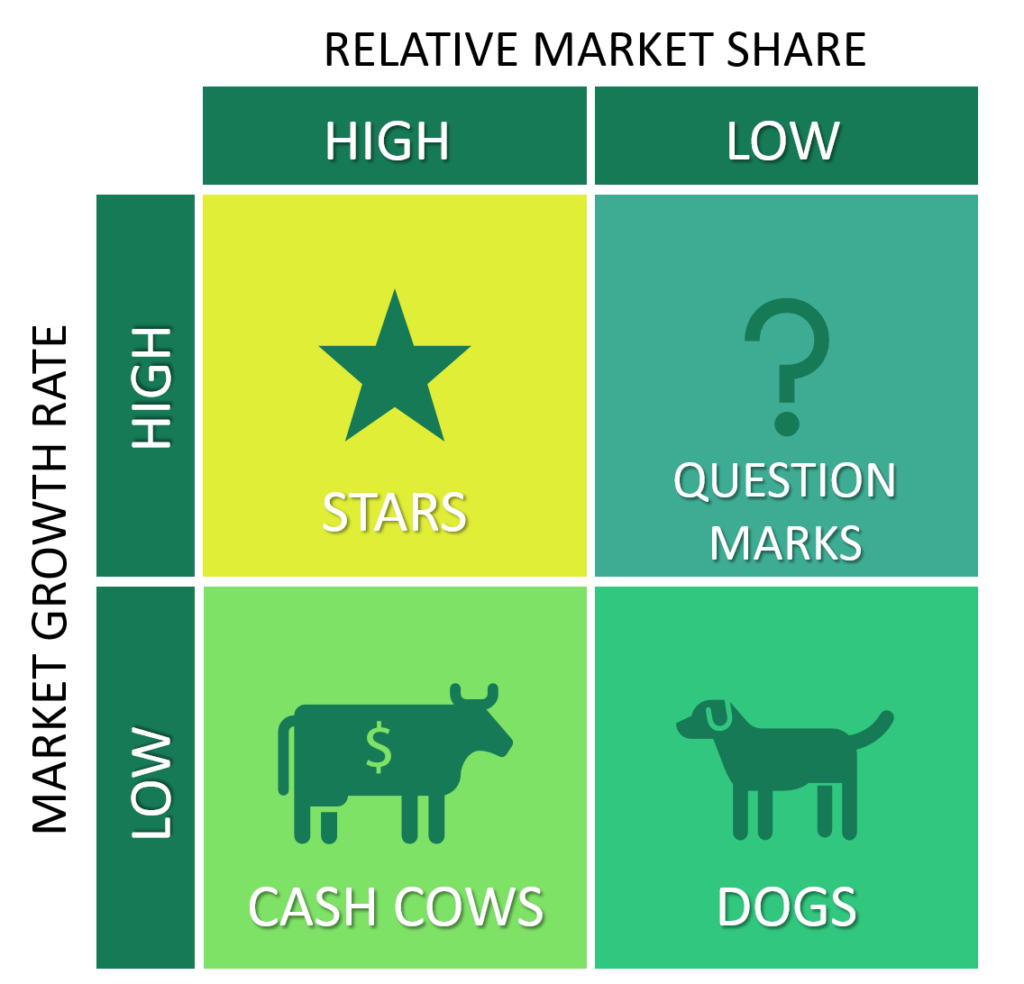
Toyota’s Global Strategy
The company’s global strategy is a remarkable journey to internationalization with effective supply chain management with astute marketing. The company’s approaches also contribute to sustainable global success. Toyota’s Internationalisation journey has targeted various regions and tailored to regional characteristics (Nkomo, 2019).
Regional Focus
The company’s internationalization began with its home market Japan. The company quickly expanded to Asia in its beginning. The market with diverse areas provided a platform for Toyota to test and adopt its products that suit various consumer preferences. Asia remains the vital region that connects its growth and development. North America also plays a vital role in global strategy. The U.S. market also becomes a landmark decision. Toyota’s investment facilities and research development centers in North America underscore its commitment to the region. The popularity of models such as the Toyota Camry and Corolla expanded the brand’s presence in North America. Europe also become a vital market that dedicates its environmental journey to hybrid technology and introduced models such as Toyota Prius that align with Europe’s growing emphasis on sustainability. Even the European strategy showcases adaptability with local market dynamics (Mordue & Sweeney, 2020).
Modes of Entry
Toyota’s choice market entry modes are also well-calibrated in each region. Joint ventures also preferred mode in some markets and allowed Toyota to partner with local companies that navigated unique challenges. Even in China, Toyota has engaged in joint ventures with local automakers that enabled access to the vast Chinese market and benefited from the local partner’s knowledge (Kawai, 2022).
Subsidiaries also played a vital role in North America, Toyota established subsidiaries and offered greater control over operations that align with Toyota’s commitment to quality and efficiency. Toyota’s supply chain management is driven by many principles by TPS that become the cornerstone to competitive advantages. The company’s approach to supply chain management reflects a commitment to quality and efficiency.
Global Manufacturing and Distribution
Toyota’s manufacturing footprint spans the globe with facilities in numerous countries. This global presence allows Toyota to produce vehicles closer to the market minimise transportation costs and enable swift responses to market demand. Toyota’s supply chain success is lean production principles. The JIT just-in-time and Kanban system redefined manufacturing efficiency worldwide. This system reduces waste, improves production flow, and enhances quality control. Toyota’s adherence to its principles of competitive advantage to set industry standards. Branding and positioning Toyota’s build on a reputation for quality, reliability, and innovation. This consistent branding is the critical element to global success. The introduction of the Lexus brand for luxury vehicles will demonstrate diversification and positioning (Dzienis & McCaleb, 2022).
Market Segmentation and Customer Targeting
Toyota has excelled in its market segmentation and offers a wide range of vehicles to cater to different customer preferences. This strategy will enable them to target diverse customer segments and maintain a global market presence. The company’s commitment will develop hybrid and electric vehicles that align with changing consumer preferences with regulatory demands. Toyota’s global strategy will inspire the successful adoption of internationalization and supply chain management with marketing strategies that will excel the global automotive industry (Kim et al. 2020). Toyota’s regional focus on entry modes with lean production to principles, branding, and market segmentation also contributes to global dominance. Understanding global strategy also provides valuable insights that aim to compete on a global scale and adapt to market dynamics.
Competitive Advantage
The company’s competitive advantage is rooted in key elements that are consistently propelled by the forefront of the global automotive industry. The company’s unwavering commitment to its reliability and quality helps to make a competitive advantage. The reputation of the company is built on its standard production of vehicles that stand on the test time which has been instrumental in building trust among consumers (Malagihal, 2021). The company’s rigorous quality including its production system ensures that each vehicle must meet its high standards and durability. Real-world data supports the element of competitive advantage with longevity and the resale value of Toyota vehicles are well-documented. Many consumer studies consistently rank Toyota as a brand associated with long-term value. These qualities also attract the customer and lead to the brand’s repeat purchase and loyalty. Cost efficiency and Economics of Scale Eagles to offer high-quality vehicles at competitive prices. Toyota’s approaches to production are characterized by the JIT system and lean manufacturing that reduced waste and improved overall efficiency. Minimizing inventory and reducing production costs enhances process efficiency. Toyota is also enable to control the costs and offer attractive pricing to consumers. Economic scale strengthens competitive advantage. One of the largest automakers can spread fixed costs over vast production volume resulting in lower average cost per unit. Toyota’s ability to balance the quality and well-built vehicles at prices that appeal brand spectrum of consumers. Innovation and sustainability are also integral parts of Toyota’s competitive advantage. The company is the leader in introducing innovative technologies and enhancing vehicle safety and fuel efficiency with performance. The development and promotion of hybrid technology also exemplifies Toyota Prius and underscores Toyota’s dedication to sustainable mobility (Kuo, 2021).
A real-world data example of Toyota’s Competitive advantage. Quality and reliability are showcased by the longevity of vehicles with many road decades after purchase. The brand’s consistent with high-ranking dependability surveys like consumer reports and J.D. Power that validate advantage. Cost-efficiency Toyota’s impressive financial performance with competitive pricing is evident in global sales. The company can maintain profitability by offering vehicles at competitive prices will demonstrate a cost-effective approach. Innovation by Toyota’s leadership in hybrid technology with millions of hybrids sold worldwide. Toyota’s commitment to sustainability reflects environmental initiatives including carbon neutrality in its operations and reducing the environmental footprint of its vehicle. Toyota’s competitive advantage has a multifaceted success story. It is also dedicated to cost-efficiency and quality with sustainability that helps to win the loyalty of customers that set industry standards. Toyota’s impressive real-world track helps to record data and support the global leader automotive sector (Liker, 2021).
Managerial Implications and Recommendations
Toyota’s global success with competitive advantage has been building a foundation of efficiency, quality, and innovation. Leadership in the global automotive sector with the following recommendations.
Maintaining and Enhancing Competitive Advantage
- Continuous Improvement: Toyota must remain committed to its principles of continuous improvement to lean manufacturing. This involves empowering employees to identify and eliminate waste and enhances quality and efficiency.
- Innovative Sustainability: The automotive industry is evolving towards autonomous vehicles that should continue investing in sustainable technologies. Expanding hybrid and electric vehiclesvehicles reducing emissions manufacturing and incorporating renewable energy are essential steps to a sustainable competitive edge (Knop, 2020).
- Digital Transformations: Embracing digital transformation by integrating advanced technologies like AI, and big data analytics with IoT into operations. These technologies optimize production and enhance vehicle safety and functionality will improve customer experiences.
Addressing Industry Challenges
- Supply Chain Resilience: In the disruptions of the global supply chain, Toyota should focus on building a resilient and flexible supply chain. Diversifying employing predictive analytics will anticipate disruptions will implement a contingency plan is vital and ensures critical components.
- Regulatory Compliance: Evolving environmental regulations with safety standards with emissions and safety regulations is vital to maintaining market access and consumer trust. Proactive engagement with regulators is the key to staying compliant (Soviar et al. 2019).
- Market shifts: Stay attuned to shifting consumer preferences with demand for EVs and shared mobility and driving. Toyota aligns with these trends and considers partnerships to strengthen the position that emerges in markets.
Strategies for Future Growth and Adaptation in the Global Automotive Sector
- Electrification and Autonomous Vehicles: Investing in production and development of autonomous vehicles. Toyota should consider expanding its electric vehicle autonomous driving technology will remain competitive evolving automotive landscape.
- Global Market Expansion: Exploring growth opportunities and emerging with marketing strategies. Developing local strategies including product offerings to meet regional preferences for future growth (Dave, 2020).
- Mobility Services: Diversify beyond traditional car manufacturing with mobility services like ride-sharing, car-sharing, and mobility-as-a-service. These services gaining traction to leverage its expertise in evolving markets.
Toyota’s Continued success global automotive sector hives towards commitment to quality. Cost-efficiency, innovation, and sustainability. Proactively addressing industry challenges strategically positioning to future growth adaptation. Toyota remains to global leader rapidly evolving with the automotive landscape.
Conclusion
Toyota’s global strategy with the competitive advantage will unveil a compelling narrative of the company’s adeptly navigating complexities in the global automotive industry. Toyota’s global success rests on its unwavering commitment to quality, innovation, and sustainability. The key elements of Toyota’s competitive advantage include reliability and quality, innovation, and sustainable practices as a global frontrunner. The company’s dedication will maintain the highest standards of durability alongside efficiency in production with lean manufacturing principles. Toyota’s competitive advantage lived reality. The brand’s longevity and global sales figures with leadership and sustainable technologies attest to its influence on the global automotive landscape. Strategic significance in global business cannot be overstated. Internationalization strategies with supply chain marketing tactics make valuable lessons for businesses to excel in the dynamic global marketplace. The company’s adaptability and commitment to innovation to industry challenges position become a beacon for global enterprises to succeed rapidly evolving world.
Reference
Ichijo, K., & Kohlbacher, F. (2020). The Toyota way of global knowledge creation the’learn local, act global’strategy. International Journal of Automotive Technology and Management, 7(2-3), 116-134.https://www.inderscienceonline.com/doi/abs/10.1504/IJATM.2007.014970
Khan, A. (2019). Enhancing Global Competitiveness through Employees: A Case Study of Toyota Motor Corporation. Editorial Committee, 82.https://www.eaim.edu.sg/images/publications/SMJ/SMJ-6.pdf#page=82
Kotabe, M., & Murray, J. Y. (2020). Global sourcing strategy and sustainable competitive advantage. Industrial marketing management, 33(1), 7-14.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0019850103001056
Madoh, A., Alenazi, J., Alkhamees, L., & Panwar, A. (2019). Case study on market mix strategies of Toyota Motor Corporation. Asia Pacific Journal of Management and Education (APJME), 2(3), 70-78.
McMillan, C. (2019). Organizational Identity, Corporate Strategy, and Habits of Attention: A Case Study of Toyota. Strategic Management: A Dynamic View, 1-20.https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=_zj8DwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA61&dq=Global+Strategy+and+Competitive+Advantage:+A+case+study+of+Toyota&ots=H7FXOUEa-x&sig=Akz4KKomjgZSr-8u1xRMMBvc_gE
Ondeng, T. O. 2020.Case Study Critical Analysis for Toyota Motor Corporate Strategy.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Tonny-Ondeng/publication/363659699_Case_Study_Critical_Analysis_for_Toyota_Motor_Corporate_Strategy/links/63287c8f071ea12e36467016/Case-Study-Critical-Analysis-for-Toyota-Motor-Corporate-Strategy.pdf
Gupta, A. K., & Govindarajan, V. (2019). Converting global presence into global competitive advantage. In International human resource management (pp. 431-442). Routledge.https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9781315252025-30/converting-global-presence-global-competitive-advantage-anil-gupta-vijay-govindarajan
Ayad, L., Abdelghani, M., Halali, A., & Muwafak, B. M. (2021). Artificial Intelligence as One of the Development Strategies for Business Organizations “Toyota Model”. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Business, Education and Healthcare, 3-21.https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-72080-3_1
Vijaya, A. P., & Rahayu, M. (2021). The Effect of Product Innovation and Service Quality on Competitive Advantage Mediated By Company Image (Study At PT. Toyota Astra Motor in Malang Raya).https://ijbel.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/IJBEL24-740.pdf
Alavi, A., Shokri, M., Zhiani, B., & Zhiani, S. (2020). Analysing competitive advantage of Iranian automotive industry using Porter’s diamond model, case study: Iranian car manufacturers. International Journal of Business and Systems Research, 14(3), 298-313.https://www.inderscienceonline.com/doi/abs/10.1504/IJBSR.2020.108269
Mahdy, F. M. (2020). Virtual Teams and Its Impact on The Competitive Advantage of Companies An analytical study on the research and development department of some international companies. American International Journal of Business Management (AIJBM), 3(9), 31-39.https://www.aijbm.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/F393139.pdf
Madhani, P. M. (2020). Lean Six Sigma deployment in retail industry: enhancing competitive advantages. The IUP Journal of Business Strategy, 17(3), 25-45.https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4002472
Nkomo, T. (2019). Analysis of Toyota Motor Corporation.http://dspace.vnbrims.org:13000/jspui/bitstream/123456789/2458/1/Toyota%20Case%20study.pdf
Helmold, M., & Terry, B. (2021). Operations and supply management 4.0: Industry insights, case studies and best practices. Springer Nature.https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=TAcpEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR9&dq=Global+Strategy+and+Competitive+Advantage:+A+case+study+of+Toyota&ots=PLErg_INdM&sig=RBhZeDjkm68VC1hGJLoTrB6ABA4
Mordue, G., & Sweeney, B. (2020). Neither core nor periphery: The search for competitive advantage in the automotive semi‐periphery. Growth and Change, 51(1), 34-57.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/grow.12354
Kawai, T. (2022). Evaluation of Toyota’s Strategy for Electric Vehicles in Counteracting Platformers—Based on the Theories of Dynamic Managerial Capabilities and Dynamic Platform Strategy—. Journal of Strategic Management Studies, 14(1), 67-87.https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/iasme/14/1/14_140105/_article/-char/ja/
Dzienis, A. M., & McCaleb, A. (2022). Motives behind Sino-Japanese strategic alliances in the new energy vehicles sector in the age of the Belt and Road Initiative. Asia Pacific Business Review, 1-26.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/13602381.2022.2093533
Kim, J. K., Yoon, J. M., & Lee, B. S. (2020). Assessment of Competitive Edge of Major Global Semiconductor Vendors for Self-Driving Solutions (Level 3 and Above)-Evaluation of Qualcomm. Intel, and Nvidia, Asia-pacific Journal of Convergent Research Interchange, 6(10), 165-180.https://scholar.archive.org/work/ojgvkeuqq5ddrpmr5y57qplhbi/access/wayback/http://fucos.or.kr/journal/APJCRI/Articles/v6n10/13.pdf
Malagihal, S. S. (2021). Strategic Options for Automobile OEMs of Indian Origin to have Sustained Competitive Advantage: A Case of Tata Motors. International Journal of Global Business and Competitiveness, 16(2), 139-152.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42943-021-00029-5
Kuo, T. N. (2021). Business model of competitive advantage. Journal of Advanced Management Science Vol, 9(1), 11-16.http://www.joams.com/uploadfile/2021/0319/20210319050403698.pdf
Liker, J. K. (2021). Toyota way: 14 management principles from the world’s greatest manufacturer. McGraw-Hill Education.https://www.accessengineeringlibrary.com/content/book/9781260468519
Knop, K. (2020). Importance of visual management in metal and automotive branch and its influence in building a competitive advantage. Polish Journal of Management Studies, 22.https://yadda.icm.edu.pl/baztech/element/bwmeta1.element.baztech-e0f8ac15-ce91-4f98-b89d-473d527ce5da
Soviar, J., Holubčík, M., Vodák, J., Rechtorík, M., & Pollák, F. (2019). The Presentation of Automotive Brands in the On-Line Environment—The Perspective of KIA, Peugeot, Toyota and VW in the Slovak Republic. Sustainability, 11(7), 2132.https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/11/7/2132
Dave, P. Y. (2020). The history of lean manufacturing by the view of Toyota-Ford. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, 11(8), 1598-1602.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Pranav-Dave-4/publication/344460563_The_History_of_Lean_Manufacturing_by_the_view_of_Toyota-Ford/links/5f787daa299bf1b53e09c53a/The-History-of-Lean-Manufacturing-by-the-view-of-Toyota-Ford.pdf
Appendices
Appendix 1: