This article will guide you on how to create a business research methods – research proposal for an MBA or other management/business degree using an example. The topic of the research proposal is – “Benefits and Challenges of Inter-Cultural Team Working in a Virtual Environment.” The document represents a sample of the high-quality assignments we offer. Specifically tailored for a student pursuing an MBA in International Business. The work will help in understanding various aspects of a comprehensive research proposal.
Business Research Methods – Sample Research Proposal for MBA
The topic of the research proposal is – “Benefits and Challenges of Intercultural Team Working in a Virtual Environment.”

In an era where cross-border collaborations are the norm, understanding the dynamics of inter-cultural teams, especially in a virtual environment is crucial. It addresses key areas such as communication barriers, leadership challenges, technological reliance, and cultural synergies that enhance team productivity. The proposal aims to understand how diverse teams can effectively collaborate in virtual environments and what are the benefits and challenges.
Also Read Dissertation Proposal Example – How to Write a Research Dissertation Proposal
Table of Contents
Benefits and Challenges of Intercultural Team Working in a Virtual Environment
1: INTRODUCTION
1.1 Introduction
Considering the landscape of high-functioning work culture, the importance of structured teamwork is always being recognized. This particular aspect has emerged enormously by following the global pace of digitalization. This particular context has been recognized to be directly associated with the influences on the performance of a particular organization. The core of this particular study has thus been selected as the interception of the entire aspect of the team working in a virtual environment. This particular aspect selected for the present study has been carried out in terms of addressing the benefits and hurdles encountered by the virtual environment for a particular work culture.
1.2 Research background
Virtual teams have been recognized to be directly linked to the ultimate enhancement of every single aspect of certain work culture. This particular aspect has been mentioned by various resources addressing the uplifted productivity of virtual teams. According to Oztemel and Gursev (2020), the core of communication channels has been digitalized and it eventually increases the existing robustness of a certain team. Considering the inter-cultural aspect of “online intercultural exchange“, the entire landscape has been shifted to an “internet-mediated intercultural engagement” often referred to as VE. It has become evident that intercultural activities encounter a massive transformation due to the absolute improvements in “goal-setting nature“. This particular aspect can easily be justified by figure 1.2.1 as the share of global organizations integrating virtual environments has experienced a massive hike between the timeline of 2014 and 2020.
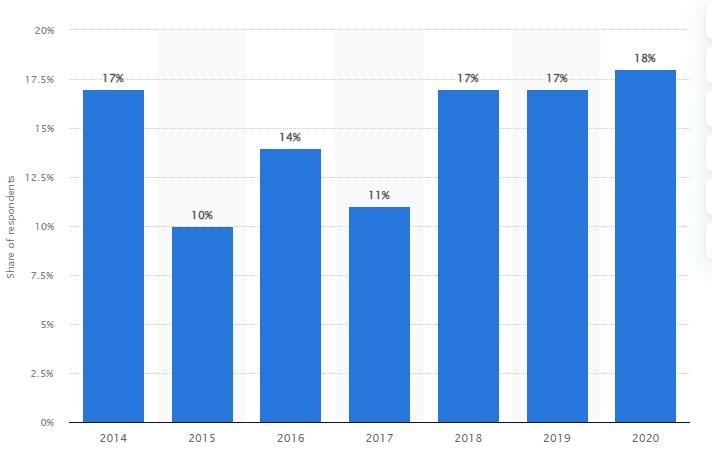
(Source: Statista, 2022)
1.3 Rationale
Digital technologies have been recognized to be linked with a particular prerequisite in terms of addressing digital teamwork. As suggested by Zeuge et al. (2020), the virtual environment plays a pivotal from the perception of the enhancement of trust within an intercultural aspect. This particular fact is also linked to specific drawbacks related to the gap within the necessary technical skills as intercultural characteristics have been considered (Morrison-Smith and Ruiz, 2020). It has been highlighted by various resources as high functioning technical skills related to VR play a pivotal role in the generation of hurdles in this particular aspect.
1.4 Research aim and objectives
The present study aims to intercept the hurdles and benefits that seem to have existed within intercultural teamwork within the virtual environment.
Objectives:
- To intercept the importance of key factors of structured intercultural teamwork.
- To identify the fundamental elements related to the virtual environment.
- To evaluate the impact of the virtual environment on the inter-cultural work culture.
- To analyze the benefits and challenges of integration of virtual environment from a particular aspect of inter-cultural teamwork.
1.5 Research questions
- What are the important elements related to structured intercultural teamwork?
- What are the fundamental policies related to the virtual environment?
- What is the actual correlation between virtual reality and intercultural teamwork?
- What are the challenges and benefits of the integration of VE in intercultural teamwork?
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Introduction
Intercultural teams refer to international teams including various people from different backgrounds and cultures. Intercultural teamwork can overcome cultural and language barriers and prepare projects around different countries in different time zones. In this chapter, certain key factors are described that influence intercultural team formation across organizations. Further discussion has been made to provide a definite understanding of the virtual environment in the workplace. Considering this, the following research will focus on critically evaluating the overall benefits and challenges of intercultural teams working in a virtual environment.
2.2 Key factors related to intercultural team working
Due to globalization, workplaces are drastically becoming integrated and interconnected. This situation makes cross-cultural understanding more vital for all people. To develop knowledge and skills as communicators, people have to be aware of the key factors of intercultural teamwork. Some key factors that impact most in intercultural teamwork are,
- Cultural intelligence
- Ethnic identity
- Gender roles
- Social relationships
- Cultural identity
A clear discussion about how these five factors are affected in intercultural teamwork is provided below.
Cultural intelligence
Cultural intelligence (CQ) can make people more efficient in working places beyond cultures. Innovation is necessary for increasing every organization’s performance and it is also predicted that the relationship between interculturalism and innovation is managed by cultural intelligence (Korzilius et al. 2017). Cultural intelligence facilitates a better understanding of diverse cultural schemas and therefore, helps in the integration of multiple cultural identities across teams.

Figure 2.2.1: Impact of CQ in intercultural teamwork
(Source: Korzilius et al. 2017)
Ethnic identity
Ethnic identity focuses on the interaction process of co-workers from different cultures. It defines the values of individual practices that point out with an ethnic group. It might be expressed by different symbols and behaviors.
Social relationships
Social relationships positively impact intercultural teamwork. Social tensions in intercultural teamwork were triggered through an effective unique method to encourage thought and in-depth discussion (Mittelmeier et al. 2018). It is demonstrated that social relationships between co-workers in a team decrease complexity and refer to more logical gains.
Cultural identity
Cultural identity can define the values and the different ways of doing work that a person carries with them from the place where the people were born and brought up. The different attitudes can affect intercultural teamwork.
Regulatory reforms and changing community expectations about organizational behavior have increased the emphasis on the role of culture in organizational compliance (Interligi, 2010).
Researchers are increasingly recognizing the role of culture as a source of variation in many phenomena of central importance to consumer research (Kastanakis, 2014). This review addresses a gap in cross-cultural benefits and behavior in virtual environment literature by providing a review and conceptual analysis of the effects of culture on efficiency and working virtually.
2.3 Understanding the advantages and challenges of the virtual environment in the Workplace
Nowadays virtual environments have become very popular in almost all industries. It does not have any physical existence and is not affected by any geographical boundaries. Virtual environments have been used and modified by many educators and team leaders to develop student’s and team members’ skills and knowledge respectively with a virtual experience (Liaw, 2019). Virtual Reality (VR) can allow multiple users to communicate online and create social and intercultural team experiences through the virtual environment. Virtual environments have many positive and negative impacts on intercultural teamwork and have been discussed as follows:
Advantages
People from any geographical location can easily work in a virtual environment without any obstacles. According to Gafni and Goldstein (2020), it is found that procrastination decreased after implementing virtual environments in multicultural contexts across various international organizations. Using a virtual environment in any workplace can save costs, increase productivity and a healthy work-life balance, and also increase the capacity of employee retention. Virtual environments can decrease carbon footprint and deliver services and products in a faster way. Using a virtual environment any organization can train employees from different backgrounds, mindsets, and with different knowledge all over the world.
Disadvantages
Major disadvantages of virtual environments are trust issues, the higher authority of any organization can’t meet the workers in person, and for this reason, a trust issue is created. During the COVID-19 pandemic, many workers showed a lack of interest in completing the project for feeling deserted (Yang et al. 2022). It also sometimes decreases the team power, every member of the team does the work at their own time, so the time management system is also hampered. Virtual environments make employees feel separated from the world. Along with that, team building is also identified as a difficult task in the virtual environment.
2.4 Theoretical underpinning
Tuckman’s theory
According to this theory, the process of team building is essentially carried out through a series of 5 specific steps. These involve forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. Through these steps, the ability of a team to perform effectively is defined during the entire duration of a specific project, starting from the time of recruitment of respective team members (Kiweewa et al. 2018). Forming stages involve introduction among different teammates and discussion regarding various project essentials, mainly involving individuals’ skills, project goals, and timelines. The storming stage mentions the requirement of an effective leadership strategy to deal with any anti-cooperativeness that arises during this specific stage.
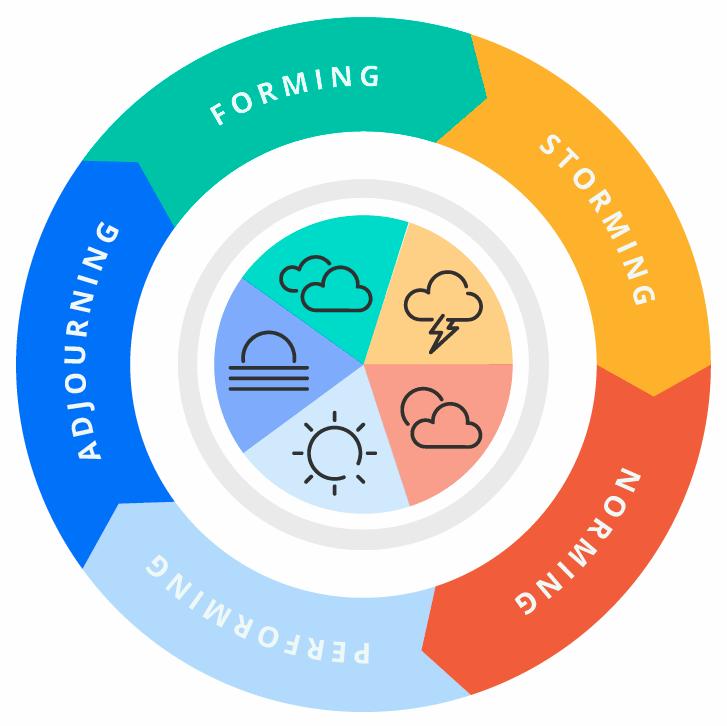
Figure 2.4: Tuckman’s Theory
(Source: Kiweewa et al. 2018)
Following this stage, team workers come to terms with every individual perspective and essentially move toward a common goal. The performing stage involves increased awareness regarding the core strengths and weaknesses of respective team members, resulting in increased motivation and work performance. Finally, the adjourning stage involves the dismissal of the team and the acquisition of a positive experience by every individual team member, allowing further work effectiveness across similar team working conditions.
2.4 Conclusion
The key factors of intercultural teamwork can be identified as cultural intelligence, ethnic identity, role of gender, social relationship, and cultural identity. A brief description of the virtual environment and the advantages and disadvantages of applying it in intercultural teamwork have been described in this chapter. The most beneficial point of adopting virtual environments is decreasing procrastination have been discussed in this section. The challenges for adopting a virtual environment in any organization are also provided.
3. SUMMARY
4. REFERENCE LIST
- Alharahsheh, H.H. and Pius, A., 2020. A review of key paradigms: Positivism VS interpretivism. Global Academic Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, 2(3), pp.39-43.
- Gafni, R. and Goldstein, A., 2020. Effects of multicultural teamwork on individual procrastination. Interdisciplinary Journal of e-Skills and Lifelong Learning, 16, pp.043-063.
- Kiweewa, J.M., Gilbride, D., Luke, M. and Clingerman, T., 2018. Tracking growth factors in experiential training groups through Tuckman’s conceptual model. The Journal for Specialists in Group Work, 43(3), pp.274-296.
- Korzilius, H., Bücker, J.J. and Beerlage, S., 2017. Multiculturalism and innovative work behavior: The mediating role of cultural intelligence. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 56, pp.13-24.
- Liaw, M.L., 2019. EFL learners’ intercultural communication in an open social virtual environment. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 22(2), pp.38-55.
- Mittelmeier, J., Rienties, B., Tempelaar, D. and Whitelock, D., 2018. Overcoming cross-cultural group work tensions: Mixed student perspectives on the role of social relationships. Higher Education, 75(1), pp.149-166.
- Kastanakis, M.N. and Voyer, B.G., 2014. The effect of culture on perception and cognition: A conceptual framework. Journal of Business Research, 67(4), pp.425-433.
- Morrison-Smith, S. and Ruiz, J., 2020. Challenges and barriers in virtual teams: a literature review. SN Applied Sciences, 2(6), pp.1-33.
- O’Reilly, C., 2021. Reflection on practice: an exploration of virtual online collaboration as preparation for the year abroad. Journal of Virtual Exchange, 4, pp.50-61.
- Oztemel, E. and Gursev, S., 2020. Literature review of Industry 4.0 and related technologies. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 31(1), pp.127-182.
- Prada-Ramallal, G., Roque, F., Herdeiro, M.T., Takkouche, B. and Figueiras, A., 2018. Primary versus secondary source of data in observational studies and heterogeneity in meta-analyses of drug effects: a survey of major medical journals. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 18(1), pp.1-14.
- Interligi, L., 2010. Compliance culture: A conceptual framework. Journal of Management & Organization, 16(2), pp.235-249.
- Statista, 2022. Use of virtual environments/ VR in market research worldwide 2014-2020. statista. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/966903/market-research-industry-virtual-environments-vr/ [Accessed on 8 May 2022]
- Walter, D. and Ophir, Y., 2019. News frame analysis: An inductive mixed-method computational approach. Communication Methods and Measures, 13(4), pp.248-266.
- Yang, L., Murad, M., Mirza, F., Chaudhary, N.I. and Saeed, M., 2022. Shadow of cyber ostracism over remote environment: Implication on remote work challenges, virtual work environment, and employee mental well-being during a Covid-19 pandemic. Acta Psychologica, 225, p.103552.
- Zeuge, A., Oschinsky, F., Weigel, A., Schlechtinger, M. and Niehaves, B., 2020. Leading Virtual Teams–A Literature Review. Von https://www. microsoft. com/en-us/research/uploads/prod/2020/07/NFW-Zeuge-et-al. pdf am, 3, p.2020.
Also Read An Analysis and Evaluation of LEGO’s Global Marketing Strategy

