Table of Contents

1. Introduction to the Business
Lego has established itself as one of the top toy manufacturers in the world, with the mission statement “Only the best is good enough.” It was founded in 1934 by a carpenter from Denmark, Ole Kirk Christensen, with the philosophy that “good play” supplements a child’s life and his subsequent life. Based on this philosophy, Lego has developed and sold a wide range of products that aim at learning and development through play.
The oldest product that has been consistently at the center of Lego’s sales is the interlocking brick set that children can use to assemble buildings, architecture, vehicles, and other such things. These bricks come in a variety of different sets and themes. The company has maintained consistency in its quality globally and has gained a strong influence in the international market.
Note: Do you need any Assignment Help at affordable prices? Contact us!
Globalization is completely transforming the business strategies followed by companies and entrepreneurs globally because of their interaction with different professional cultures and socio-cultural factors affecting their businesses (Triandis, 2007). Lego has adapted to global business practices and marketing strategies, which have helped it sustain itself in the long run. While the product offering of Lego is unique, the key to the company’s global success is also driven by its focus on marketing (Simon, 2017).
The following report is intended to analyze and evaluate Lego’s global marketing strategy and demonstrate how the organization strategically manages its marketing operations across global markets and different cultures. It also aims to explain the strategies behind the profits of the company, as shown in Figure 1. The report uses statistics from verified sources and examples from the experiences of various companies to justify its analysis. It provides a detailed overview of the company’s global strategies using environmental analysis, a brief marketing mix, and the product portfolio.
2. Company capability and product/service portfolio
2.1 Product Portfolio:
The company has sold its toys for generations, and the children who once played with them are now even working for the company. With these years of legacy, Lego has managed annual sales of approx. 5 billion dollars in the year 2020 (Lego, 2020). Lego has been under pressure to change its general strategy and products in recent years due to digitalization and competition. However, the basic product and its design have essentially been unaltered. Lego provides toys in the form of multi-colored blocks and pieces that can be used by children to construct structures and thematic designs.
The Lego brick sets and thematic products are among the cash cows of the company and contribute to the majority of sales, and even with low market growth, the company has a major share in these products. Apart from the bricks, the company produces thematic toys like cars and action figures compatible with the brick set. These comprise the majority of the company’s earnings (Anon., 2021).
Another product with good revenue generation capacity is the Legoland Discovery Centers, which are indoor family attraction chains inspired by Lego brick designs. These are smaller versions of Lego theme parks that produce good revenue. Mindstorm NTX is the robotic division of Lego and the first of its kind to enter the market. Despite having many competitors in today’s market, Lego maintains one of the highest sales in the market.
Apart from these products, Lego also produces online games that attract children as well as adults. These are not high-income assets and are co-owned by several large brands. Lego needs to work more on the research and development of online games in order to penetrate the online gaming market.
2.2 Company Capability:
2.2.1 Brand Image:
Lego has an established brand image that helps with marketing across cultures. It separates Lego from its competitors due to the product quality, service, and customer experience generated. The customer-friendly image and the child-friendly products of Lego have generated high customer loyalty and faster growth in sales. This image also helps in gaining new customers easily, as trust in the brand is accepted globally.
Lego’s image is linked to the safe learning and growth of children. The brand image is firm and cannot be intimidated easily. This global brand image contributes significantly to the cross-cultural marketing success of Lego.
2.2.2 Marketing:
Lego has owed a huge portion of its success to its highly effective marketing strategies and techniques. The company’s marketing strategies can be divided into two parts: pre- and post-digitalization.
The pre-digitalization marketing strategies included store campaigns, magazine commercials, and advertisements through media channels like television and comics. However, the company fairly adjusted its approach to digital marketing with the onset and increased usage of the internet amongst children and their parents. Lego now utilizes both traditional marketing channels as well as digital marketing channels to market their product. Additionally, initiatives like Legoland Discovery are very successful in capturing the attention of potential customers.
2.2.3 Intellectual Property:
Lego patented its chief product, the Lego bricks, back in 1959 and has held the rights ever since. This provides Lego with an unmatched advantage in the toy industry, and no other company has created products for its competition since. Lego also holds various patents for its other unique products and consistently invests in research and development of newer and better toys. Having intellectual rights over product designs has helped Lego in the long run by offering unique products.
2.2.4 Human Resources:
Lego has employed a very capable and efficient workforce, and human resources provide a strong edge to the company. HR has played an important role in developing and reinforcing the work culture in the company. Lego owes its success to its staff and the work environment that they create. Figure 2 analyzes the growth of HR in the past 10 years.
To be effective in global marketing, Lego needs to have a diverse environment in the workplace so that employees have an outlook towards the different cultures across the world and can adjust the product and marketing according to the culture. Also, diversity in the workplace has proven to bring more creativity and better ideas to the company. Most global companies are focusing on their HR aspects, and Lego needs to keep up to maintain its position in the market.
3. Market and environmental opportunities and characteristics
3.1 The Economic Factors:
Economic factors are one of the central factors affecting the growth and sales of international brands. Economic factors play a vital role in shaping the markets and economies of the regions. They decide the spending capacity and priorities of the customers. The present economic factors play an important role in identifying the opportunities and hazards presented by global trade. In good economies, customers can purchase non-essential products, and the sale of such products is observed to be very high in booming economies. On the other hand, countries and regions with declining economies show lower levels of economic activity in the market. Low employment restricts customers from sticking to essential items of need.
The past few years have shown a rising economy globally, which is accounting for the increased global sales of Lego. However, the pandemic has caused unemployment in many nations, including the UK and the US. The pandemic has had a dramatic swing in the sales of Lego recently. The digitalization, however, helped the company beat the effects of the situation. Still, the lack of jobs and reduced average incomes pose a threat to the sales of the company.
3.2. The socio-cultural factors:
Socio-cultural factors also play a significant role in global businesses. Culture and social norms determine the market preferences of the people. For example, Japanese culture is inclined towards ecological products and recycling, so companies need to change their product packaging accordingly to succeed in the Japanese market.
Technology and digitalization are constantly changing the needs of customers. Parents are now more focused on their children’s overall growth. Parents are relying on technology and smart technological tools and toys for this, which gives Lego a strong opportunity. Having already mixed its physical and digital products, Lego is adapting to the new social norms. Similarly, cultural norms play an important role globally and need specific strategies to ensure better opportunities.
3.3. The Competitive Environment:
Lego has a slowly growing competitive environment as technological growth is offering opportunities to many companies in the toy market. With growing digitalization, children are more attracted to technological toys and screens than physical toys. Lego has managed to keep up with this type of competition due to its customer loyalty and product quality. Toy brands like Fisher-Price, Barbie, Nerf, Hasbro, and others pose a challenge to Lego. A detailed analysis of brand value is shown in Figure 3.
Apart from similar toy companies, Lego also faces competition from educational game companies and video game companies like Play Station and LingoKids. Lego is facing competition in the international market. The company needs to invest more in its research and development and focus on increasing the domain of toys and developing more innovative sets and games.

4. Marketing Strategies and Tactics
4.1 Market selection: key markets and target customers
Market selection is the key to the fast penetration and growth of a company (Porter, 2018). It helps define the size of the market and the potential the market holds in terms of sales and profits.
Lego has an audience in America, Europe, the Middle East, Africa, and the Asia Pacific. The audience for the majority of its products lies between the ages of 3 and 15. Lego has successfully launched toy bricks and thematic action figures and sets for children, adolescents, and young teenagers. The pricing and complexity of the toys vary for different ages. The older audience is more engaged in complex, motorized toys that come at a higher price, while younger children are attracted to simpler toys with lesser complexity, which come at lower prices.
The target audience is from upper- or middle-class families, as the products are costly and therefore have a specific target customer base (Pratap, n.d.). Lego has also introduced a variety of video games that fascinate adolescents and teenagers from all sections of society. In general, it can be said that Lego has a very wide target audience across the globe.
4.2 Mode of market entry for Lego
Lego has a globally recognized marketing strategy that accounts for its easy market penetration in different cultures. The company uses both traditional and modern strategies to drive faster growth. Lego owns hundreds of retail stores globally that account for offline sales, while they also utilize digital channels to sell their products (Green, 2013). The Lego online store and digital marketing techniques account for successful sales through the internet. Lego uses online as well as offline sources for promotion and sales, which helps them keep up with technology while not losing their traditional customers. Lego has various reward and loyalty programs that drive customer participation and loyalty. For example, Lego allows customers to submit their designs, out of which four are chosen annually and manufactured, and the designer gets a 1% sales profit from the product. Strategies like these have helped Lego maintain a stronghold on the market and strengthen its brand awareness globally. Other strategies include:
4.2.1 Direct Export –
Companies use this method when they have no means to establish infrastructure in other countries, so they export the manufactured product directly to those countries. Lego exports products from countries like Norway and the UK.
4.2.2 Franchising –
During global expansion, the company name might not be established in the target country. Under such conditions, companies sometimes use franchising to sell their products under the name of an established company. Lego uses franchising in some Asian countries, but not extensively.
4.2.3 Licensing –
The process of licensing involves giving rights to firms or companies with a large market share in a market rather than competing with them. Licensing involves the production allowance of specific products and services only. Lego has entered into licensing agreements with various companies (Lego, 2020).
4.2.4 Partnership
A partnership is an attractive option when both companies have expertise in different domains and can combine them to produce better products and create better opportunities. Lego has entered into partnerships with various companies like Adidas, Levis, and Warner Bros. in the field of marketing and promotion (Lego, 2020). Such partnerships are mutually beneficial.
4.3 Marketing Mix (3 P’s of Marketing for Lego)
Lego has been consistent in its strategic planning of the marketing mix to penetrate markets. Marketing mixes refer to the strategies that companies use to promote their products or services in the market. A marketing mix helps businesses plan a successful product offering by analyzing their strengths, avoiding useless costs, executing effective marketing strategies, understanding the needs of customers, and planning when and how to promote the product (Lahtinen, 2020).
4.3.1 Product
The product is a commodity (like edibles, electronics, etc.) or a service (like security, transportation, etc.) that the company offers. The product is defined by the exact commodity or service provided along with its pre-negotiated prices (David Oliver, 2007). A product is defined by its quality, brand, manufacturing, presentation, and price. The adoption of a product in any culture mostly depends on how relatable it is to the people or how conflicted it is with their opinions and ideologies (Waterschoot, 2015).
The products Lego offers have significantly changed over the past few years. From the typical brick sets, Lego has shifted to complex mechanized toys as well as online video games. Offering toys like Mindstorm Nxt2.0, theme sets, car sets, and other such toys is setting Lego apart. Also, by partnering with companies, Lego is creating theme sets like the Toy Story, and Marvel superhero theme sets, etc. (Lego, 2020). This way, Lego is increasing its domain and subsequently modernizing its products as well.
4.3.2 Price
The pricing strategy of the product determines the cost margin and the profits, and it is important to strategize this aspect keeping various cultural and economic factors in mind (Armstrong, 2019). Lego has a majority of its products for children and teenagers between the ages of 3 and 15. These products are aimed at middle-class and upper-class families. So, the products are not cheap and come at a cost. The products are designed and produced with high precision and quality and have a very long life.
Production and testing are vigorous processes that come at a cost to the company, which justifies the high pricing of the products. However, they are not very heavily priced, as they have to be affordable to most of the children and their families. The high quality justifies the price and creates great value for the customer, so they come back again and the company gains great market share through repeated purchases.
4.3.3 Promotion
Promotion refers to the strategies the company uses to communicate its products and services to the public. It also involves strategies to lure the customer to prefer the product over other similar products available on the market (Kotler, 2015). The strategies involved in the promotion can be marketing, advertisement, direct one-to-one marketing, other means of promotion, or all of these (Porter, 2018). Lego uses a variety of methods, ranging from innovative digital methods like social media marketing to traditional methods like television advertisements, for its promotion.
It has also partnered with many brands, like Warner Media, Disney, and Adidas, for joint promotions. The company has achieved strong brand awareness throughout the globe and remains a favorite of kids aged 3 to 15 years old. The promotional strategy of Lego has proved to be the driver of global success. Lego has set itself apart from other toy companies with its innovative methods. Recently, Lego entered into a partnership with film companies like Universal and Warner Bros. to increase its global brand awareness.
5. Recommendations for Lego’s Market (for the next 5 years)
5.1. Markets
80% of the toy revenue for Lego comes from Europe, America, and Central Asia. Lego has a global market share of 8.6% in toys, which gives it a good name in other countries as well. Lego has potential markets in Australia and rich African countries where it can invest in the coming years. It will be important to keep regional demands and customer behavior in mind before stepping into these markets.
5.2.Pricing Strategy
The Lego pricing strategy has been effective for Western and first-world countries. Lego targets kids from affluent families. However, in Eastern and Asian countries, the products appear more costly than the available toys on the market. The company should revise its products and pricing accordingly to penetrate markets in potential countries like Japan, China, Pakistan, and India. These countries have a considerably higher population of children, as their demographic is on the younger side. Thus, the market potential in these countries is vast, and a good pricing strategy is essential to gaining those potential customers.
5.3 Attracting females toward the product
Nearly 80% of Lego consumers are male (Arturo, n.d.). The products offered by Lego are somewhat gender-biased when it comes to thematic products. Lego has focused on producing various male superhero character-themed products but has lacked female counterparts or equivalents. Similarly, the video games by Lego are too violent to attract female kids. This leads to the female kids being attracted to products from other brands that are specifically designed for them.
Lego should focus on this aspect to make necessary changes in their product themes and introduce female-friendly characters as well as themes that girls will be better able to relate to.
5.4 Promotion
Promotion through traditional methods is not enough for Lego. With global digitalization, children and their parents all over the world are using the internet regularly. Lego can utilize these channels apart from its digital marketing and promote its product through social marketing channels as well as through influencers and blog writers who influence potential customers.
5.5 Entering markets through partnerships
Lego has avoided sales agreements in most major Eastern and Asian markets, which has hindered the company’s expansion. On the other hand, companies like Hamleys have gained significant growth in Asian countries by partnering with regional companies. To manage the negative impacts of political influence, Lego must enter into tie-ups and partnerships with regional companies in Asian countries like Japan and India to increase their sales. Such companies are more acquainted with the local shopper’s attitude and will be able to market the products more easily, and the regional company name will also foster trust in the shoppers.
6. References
Anon., 2021. Lego defies toy sector gloom as sales and profits rise. [Online]
Available at: https://www.ft.com/content/57516281-3522-47a9-ae99-caaa049f490a
Anon., n.d.
Armstrong, G. K. P. H. M. a. B. R., 2019. Marketing: An Introduction, 4th ed. In: Marketing: An Introduction, 4th ed., Pearson UK.
Arturo, J., n.d., Issu. [online]
Available at: https://issuu.com/arturocreative/docs/lego_memoria_final
David Oliver, C. J., 2007. Developing guiding principles: an organizational learning perspective. Journal of Organizational Change Management.
Goi, C. L., 2009. A review of the marketing mix: 4Ps or more?. International Journal of Marketing Studies.
Green, K. A., 2013. Lego. In: Global Marketing, Seventh Edition, p. 497. s.l.: Pearson, p. 497.
Ho, H. F. H. C. C., 2008. Marketing mix formulation for higher education: an integrated analysis employing analytic hierarchy processes, cluster analysis, and correspondence analysis. International Journal of Educational Management.
Kotler, W. S., 2015. Principles of Marketing. MFSA Journal of Marketing.
Lahtinen, V. D. T. a. R.-T. S., 2020. Long live the marketing mix. Testing the effectiveness of the commercial marketing mix in a social marketing context., s.l.: Journal of Social Marketing.
Lego, 2020. Lego Annual Report 2020, s.l.: Lego.
Lego, 2020. Lego Inc. [online]
Available at: https://www.lego.com/en-us/aboutus/news/2020/september/interim-results/
Porter, M. E. (2018. Competitive advantage: Creating and sustaining superior performance. Harvard Business Review.
Pratap, A., n.d., Lego Marketing Mix. [Online]
Available at: https://notesmatic.com/2019/06/lego-marketing-mix/
[Accessed June 11, 2021].
Rothkp, D., 1997. In praise of cultural imperialism? Effects of globalization on culture. Foreign Policy, p. 103.
Sadykova Raikhan, M. M., 2014. The interaction of globalization and culture in the modern world. ScienceDirect.
Simon, E. A., 2017. How digital remix and fan culture helped the Lego comeback. Transformative work and cultures.
Triandis, H. C., 2007. Cultural aspects of globalization. Journal of International Management.
Waterschoot, W. v., 2015. The 4P Classification of the Marketing Mix Revisited. Journal of Marketing.
7. Appendices
1.
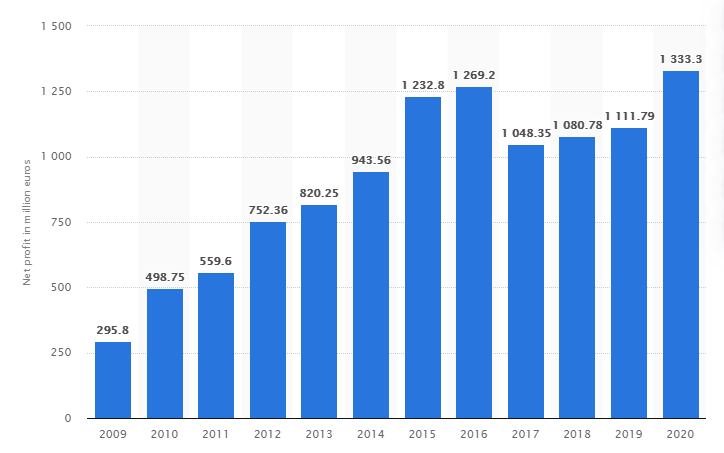
Figure 1: Net profit of the Lego company from 2009–2020 (source: Lego annual reports, 2009–2020)
2.
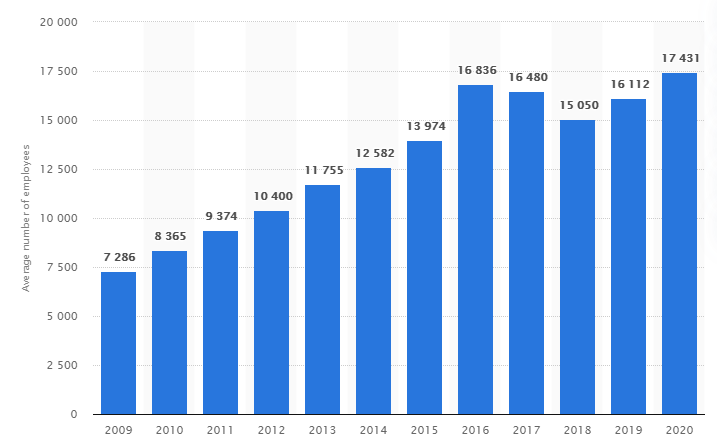
Figure 2: Average number of employees of the Lego group worldwide from 2009 to 2020 (source: Lego annual reports, 2009-2020)
3.
| Brand name | Brand value 2020 | Brand value for 2019 |
| Lego | $ 7,535 M | $6,884 M |
| Bandai Nemco | $ 1,038 M | $ 1,630 M |
| Fisher Price | $ 817 M | $652 M |
| Nerf | $ 366 M | $ 413 M |
| Barbie | $ 416 M | $ 374 M |
Figure 3: Brand value analysis of Lego with its competitors (source: Report by the Financial Times’ on the brand values of toy companies)
Also Read An Analysis and Evaluation of LEGO’s Global Marketing Strategy

